Magnetic particle testing
- This method is used to detect surface and subsurface discontinuities in ferromagnetic substances. This is also used to test the weld works.
- The component which is to be tested is cleaned first.
- After cleaning, the specimen can be magnetized either by direct magnetization or by indirect magnetization.
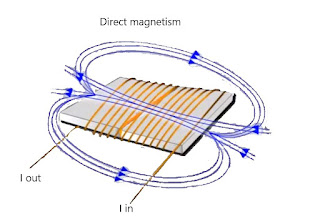
- Direct magnetization occurs when an electric current is passed directly through a specimen to produce a magnetic field.
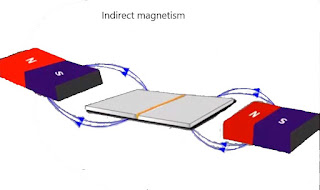
In indirect magnetization, magnetic field is applied by using a strong external magnetic field without passing current through the specimen.
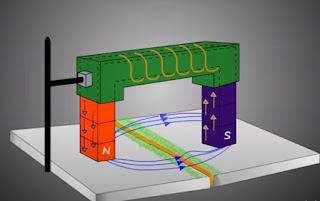
- Indirect magnetization can be done by using permanent magnets or electromagnets.
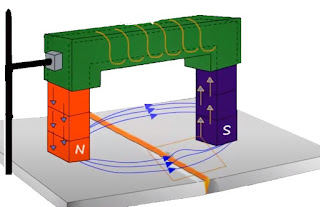
- Since magnetic fields in permanent magnet cannot be varied, electromagnets are preferred usually for testing.
- Electromagnet consists of a coil of wires through which current is supplied to produce a magnetic field.
- The amount of magnetic field produced depends on the amount of current passed through the coil.
- Magnetic flux created, is used to detect the flaws in the specimen.
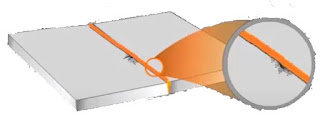
- This flux lines running along the surface will deviate from the path if it approaches a crack.
- Fine magnetic particles are applied to the surface of specimen for visible indication of cracks.
- These fine magnetic particles are attracted to the area of flux deviation, creating a visible indication of flaw.
- Simplicity of operation is the main advantage of magnetic particle testing.
- Major disadvantage of this method is that it is restricted to ferromagnetic substance, surface or near-surface flaws.



No comments